Learn about a treatment option that may be right for you.
5 THINGS THAT MAY CAUSE IBS-D
There are many potential causes of IBS-D, but the exact cause is unknown.
Below, explore 5 reasons why you may be experiencing symptoms. Understanding your symptoms and more about your gut microbiome is one way to get gut-smarter about your condition.
Click to dive deeper on the possible causes of IBS-D.
Gut microbiota Gut-brain axis Immune system Family history Anxiety / depression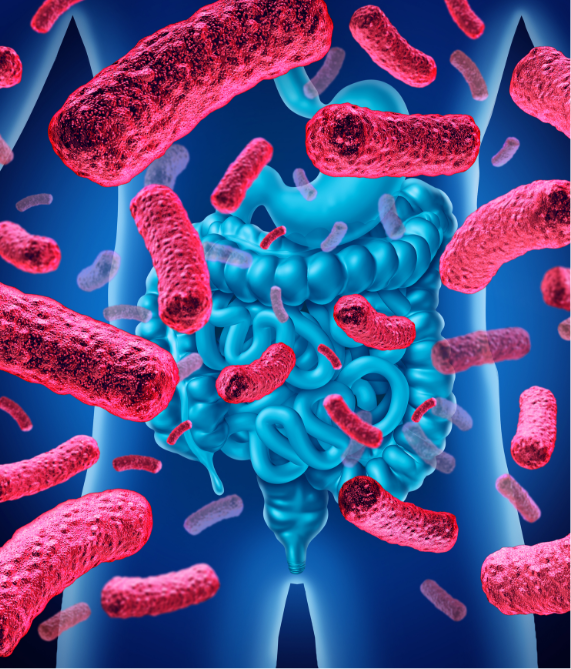

Imbalances in the gut microbiota
Some studies suggest that an imbalance in the usual amount of healthy bacteria in the gut may be found in people with IBS-D. This imbalance can be related to genetics, infection or disease, anxiety, diet, drug use, or other causes.
DID YOU KNOW?
A study of over 100 people with IBS showed that 73% of people with IBS had an imbalance in their gut microbiota, compared with only 16% of healthy people.
Communication problems between the brain and digestive system
There is a 2-way communication system between the brain and the digestive system, known as the gut-brain axis.
Normally, signals go back and forth between the brain and the digestive system to help your body know when you have eaten enough, when to start digesting food, and when to have bowel movements.
Changes in these signals can cause problems on either the digestive or brain side, which may lead to stress, anxiety, depression, or symptoms such as pain or diarrhea.
Not an actual patient.
Problems in the immune system
Activation of the immune system can cause inflammation that might result in symptoms of IBS-D. Your immune system is your body’s defense against disease.
But if your immune system takes action in your digestive system—maybe because of an infection or stress—the lining of the digestive tract can become irritated and inflamed, causing pain and diarrhea.
Problems in the immune system
Activation of the immune system can cause inflammation that might result in symptoms of IBS-D. Your immune system is your body’s defense against disease.
But if your immune system takes action in your digestive system—maybe because of an infection or stress—the lining of the digestive tract can become irritated and inflamed, causing pain and diarrhea.
Not an actual patient.
Family history (genetics and childhood)
Certain genes associated with the immune system, inflammation, digestion, and psychiatric disease may be linked to IBS. Factors such as substantial stress experienced in early childhood could also play a role.
People with family members who have IBS are more than twice as likely to develop IBS themselves.


Not an actual patient.
Anxiety and/or depression
Many people with IBS-D feel depressed or anxious, but it can be difficult to determine if these feelings are a cause or a result of IBS-D. Some factors associated with IBS-D can cause depression, anxiety, or other mood disorders.
While other studies show that stress may cause changes in the gut microbiota and contribute to the symptoms of
Your gut has what?
Find out what’s going on in your digestive system in this video.
Discover a treatment option for adults with IBS-D.






